Deploying a dApp using the Remix IDE
This tutorial shows how to create a smart contract and a dApp using ReactJS, where the contract and the dApp will interact with each other. This two-part series discusses how to deploy a smart contract using the Remix IDE, then develop a To Do List app using ReactJS.
What is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is a program that runs on the blockchain. It is a digital contract and agreement that requires no human interaction nor trust from a third party. The smart contract in this exercise is written in Solidity. Smart contracts are executed on an EVM (a virtual machine).
What is a dApp?
A dApp (decentralized application) is an application that runs on many servers across the blockchain. dApps are mostly used in the crypto-marketplace, where they require security and transparency.
Before You Begin
To start this exercise you need to have the following apps/tools installed or available in your localhost:
Remix IDE - development tool to compile and deploy the smart contract. You can use the online version of the Remix IDE.
Note: Read the Remix documentation for usage.
Node.js - a programming environment needed to create the dApp (installation required).
Gobi Testnet (current EON network) - the EVM sidechain where the smart contract and dApp are deployed to.
Gobi Testnet Configuration
Network Name: Gobi Testnet
RPC URL: https://gobi-rpc.horizenlabs.io/ethv1
Chain ID: 1663
Use TodoList Smart Contract
The TodoList smart contract example is used to compile and deploy through Remix IDE. Later, it is used to manage the dApp (To Do List) example.
This smart contract allows you to create the To Do List (app) by storing the list of tasks as a Task structure.
The contract has two main functions:
- createTask - allows you to create a new task with content and an initial state (not completed)
- toggleCompleted - allows you to toggle the state of the task (completed or not completed)
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract TodoList {
uint public taskCount = 0;
struct Task {
uint id;
string content;
bool completed;
}
mapping(uint => Task) public tasks;
event TaskCreated(
uint id,
string content,
bool completed
);
event TaskCompleted(
uint id,
bool completed
);
constructor() {
createTask(unicode"Task Example");
}
function createTask(string memory _content) public {
taskCount ++;
tasks[taskCount] = Task(taskCount, _content, false);
emit TaskCreated(taskCount, _content, false);
}
function toggleCompleted(uint _id) public {
Task memory _task = tasks[_id];
_task.completed = !_task.completed;
tasks[_id] = _task;
emit TaskCompleted(_id, _task.completed);
}
}
Compile and Deploy the Smart Contract
In the Remix IDE, create a new workspace for the TodoList smart contract example. Perform the following steps:
In the FILE EXPLORER (side panel), click the File Explorer icon.
Select a workspace.
Click the new file icon.
Name the file, todolist.sol.
Copy and paste the smart contract example or manually enter it using the main panel.
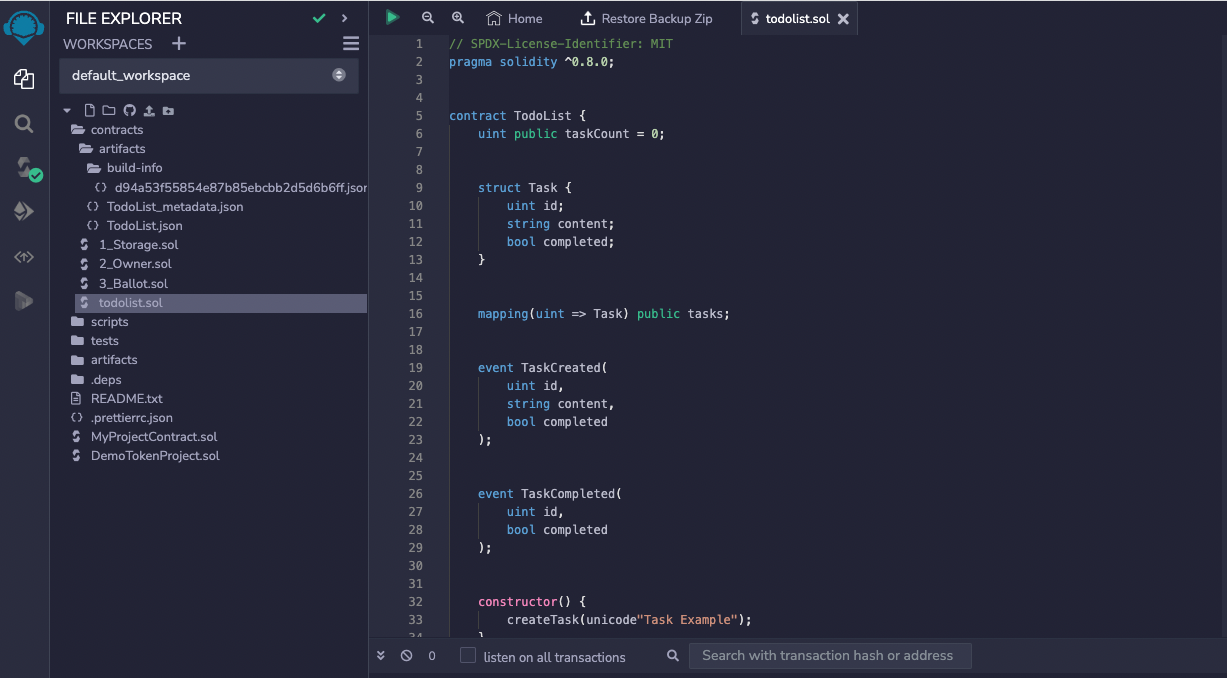
- Click the Compiler icon. The COMPILER pane (side panel) appears.
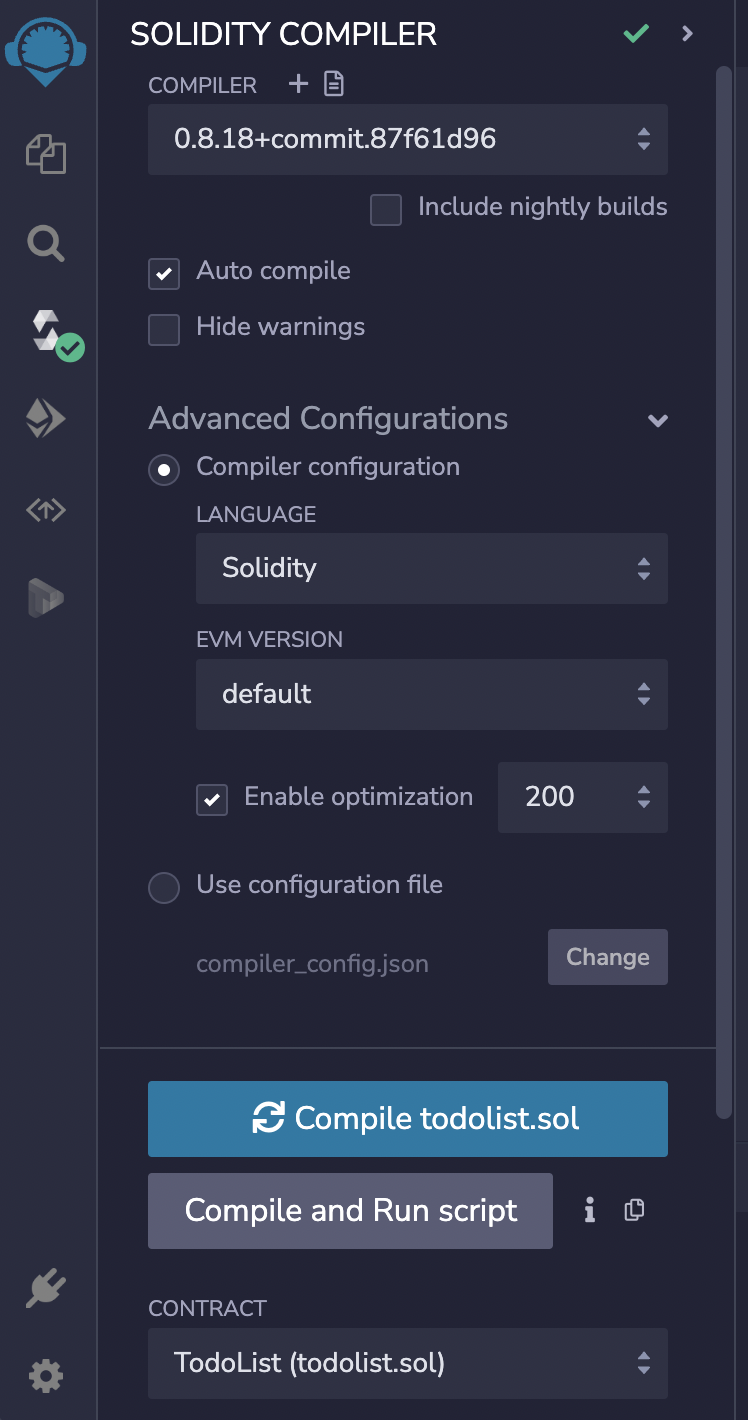
- Select the compiler version.
- In the Advanced Configuration, make sure that the Enable optimization is checked and set to 200.
Click Compile todolist.sol.
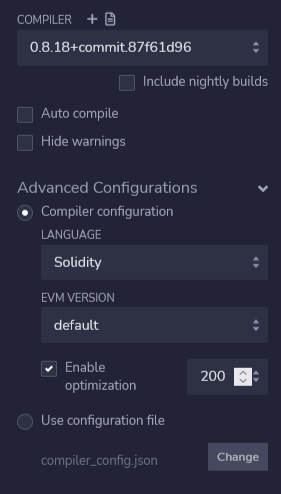
After the compilation process successfully completes, click the Deploy icon.
The DEPLOY & RUN TRANSACTIONS pane appear. In the ENVIRONMENT field, toggle to Injected Provider - MetaMask. The wallet must display the Gobi Testnet network (1663).
Note: Make sure that your MetaMask wallet has currency to pay for gas. Otherwise, copy your wallet address and go to the EON Faucet to make a request for TZEN.
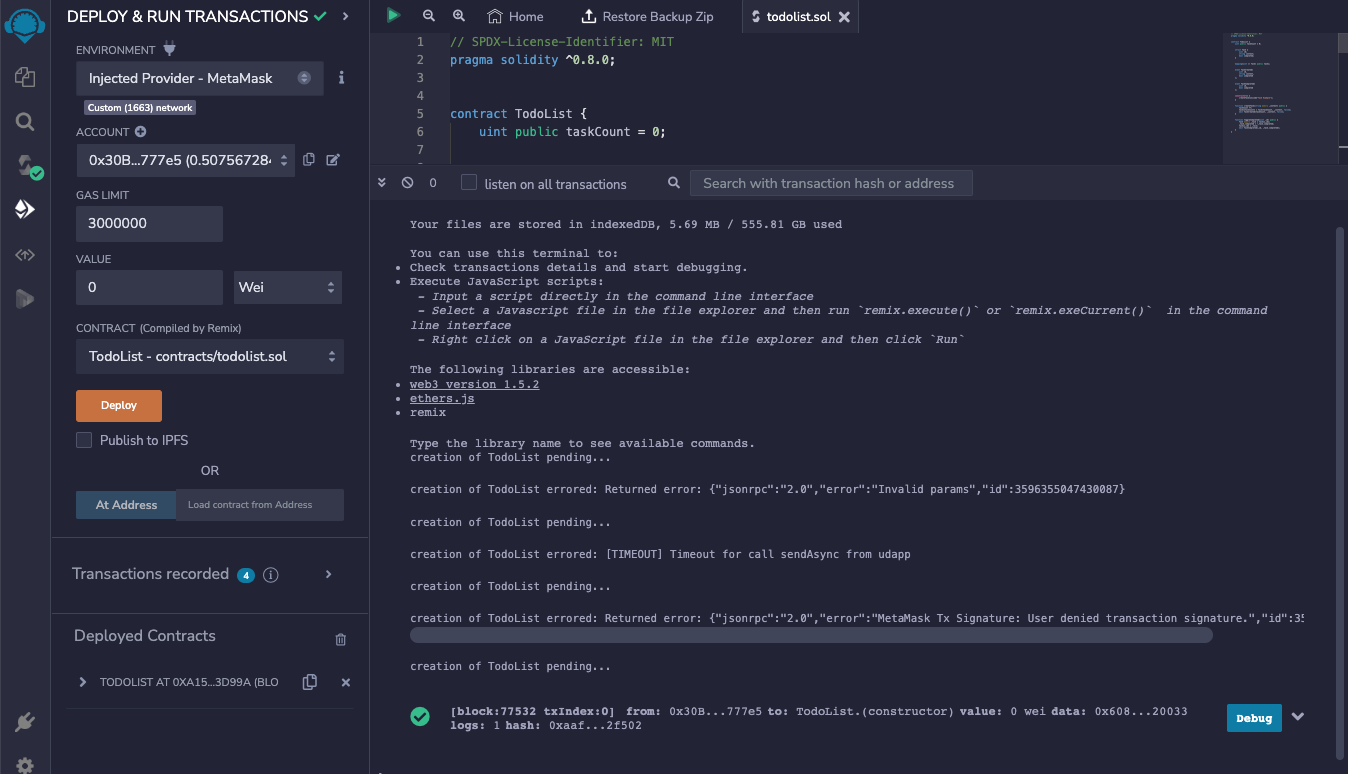
- Click Deploy. The MetaMask wallet displays a confirmation message.
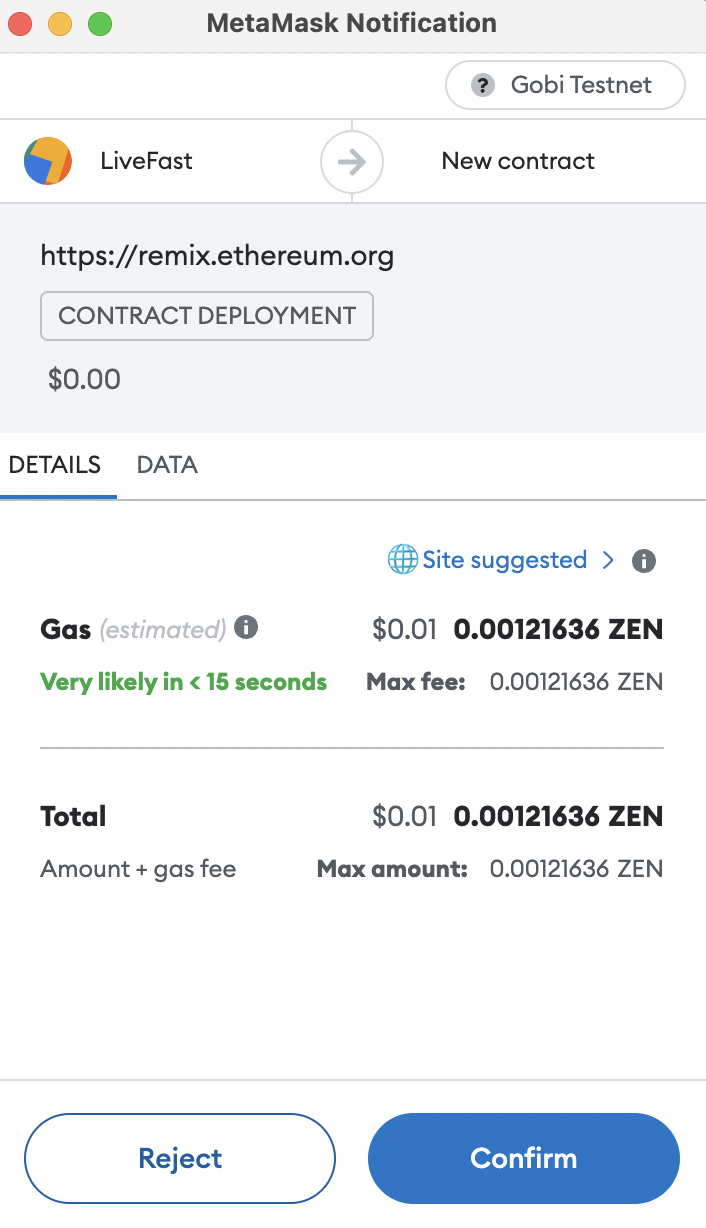
At the bottom of the DEPLOY & RUN TRANSACTIONS pane, click the copy icon (to your clipboard) in the Deployed Contracts. You will need the deployment address during the creation of the dApp.
Create the dApp using ReactJS
To begin creating a dApp using ReactJS, perform the following steps:
- Make sure that you have installed Node.js in your localhost.
- In your Documents folder (localhost), create a project directory (such as My Project) and a sub-folder called todolist.
- In a terminal window, go to the newly created todolist folder and initialize the ReactJS project by using the following command:
npx create-react-app .
npm install ethers@^5
Note: The command, npx create-react-app . only executes in the todolist directory level.
- Create a .env file in the todolist folder by using the command:
touch .env
- Use vi editor to add the line:
REACT_APP_TODO_LIST_ADDRESS="<add your contract address>"
Note: Your contract address appears in the Remix IDE under the Deployed Contract module. Click the copy icon then paste between the quotes.
In the src directory, create a contracts folder.
In the contracts directory, create a file called, TodoListABI.json.
In the Remix IDE, copy the ABI (bottom of the Compiler module).
Insert the ABI into the TodoListABI.json file.
This is an ABI file example:
[
{
"inputs": [
{
"internalType": "string",
"name": "_content",
"type": "string"
}
],
"name": "createTask",
"outputs": [],
"stateMutability": "nonpayable",
"type": "function"
},
{
"inputs": [],
"stateMutability": "nonpayable",
"type": "constructor"
},
{
"anonymous": false,
"inputs": [
{
"indexed": false,
"internalType": "uint256",
"name": "id",
"type": "uint256"
},
{
"indexed": false,
"internalType": "bool",
"name": "completed",
"type": "bool"
}
],
"name": "TaskCompleted",
"type": "event"
},
{
"anonymous": false,
"inputs": [
{
"indexed": false,
"internalType": "uint256",
"name": "id",
"type": "uint256"
},
{
"indexed": false,
"internalType": "string",
"name": "content",
"type": "string"
},
{
"indexed": false,
"internalType": "bool",
"name": "completed",
"type": "bool"
}
],
"name": "TaskCreated",
"type": "event"
},
{
"inputs": [
{
"internalType": "uint256",
"name": "_id",
"type": "uint256"
}
],
"name": "toggleCompleted",
"outputs": [],
"stateMutability": "nonpayable",
"type": "function"
},
{
"inputs": [],
"name": "taskCount",
"outputs": [
{
"internalType": "uint256",
"name": "",
"type": "uint256"
}
],
"stateMutability": "view",
"type": "function"
},
{
"inputs": [
{
"internalType": "uint256",
"name": "",
"type": "uint256"
}
],
"name": "tasks",
"outputs": [
{
"internalType": "uint256",
"name": "id",
"type": "uint256"
},
{
"internalType": "string",
"name": "content",
"type": "string"
},
{
"internalType": "bool",
"name": "completed",
"type": "bool"
}
],
"stateMutability": "view",
"type": "function"
}
]
At this point, your directory structure should look like the following:
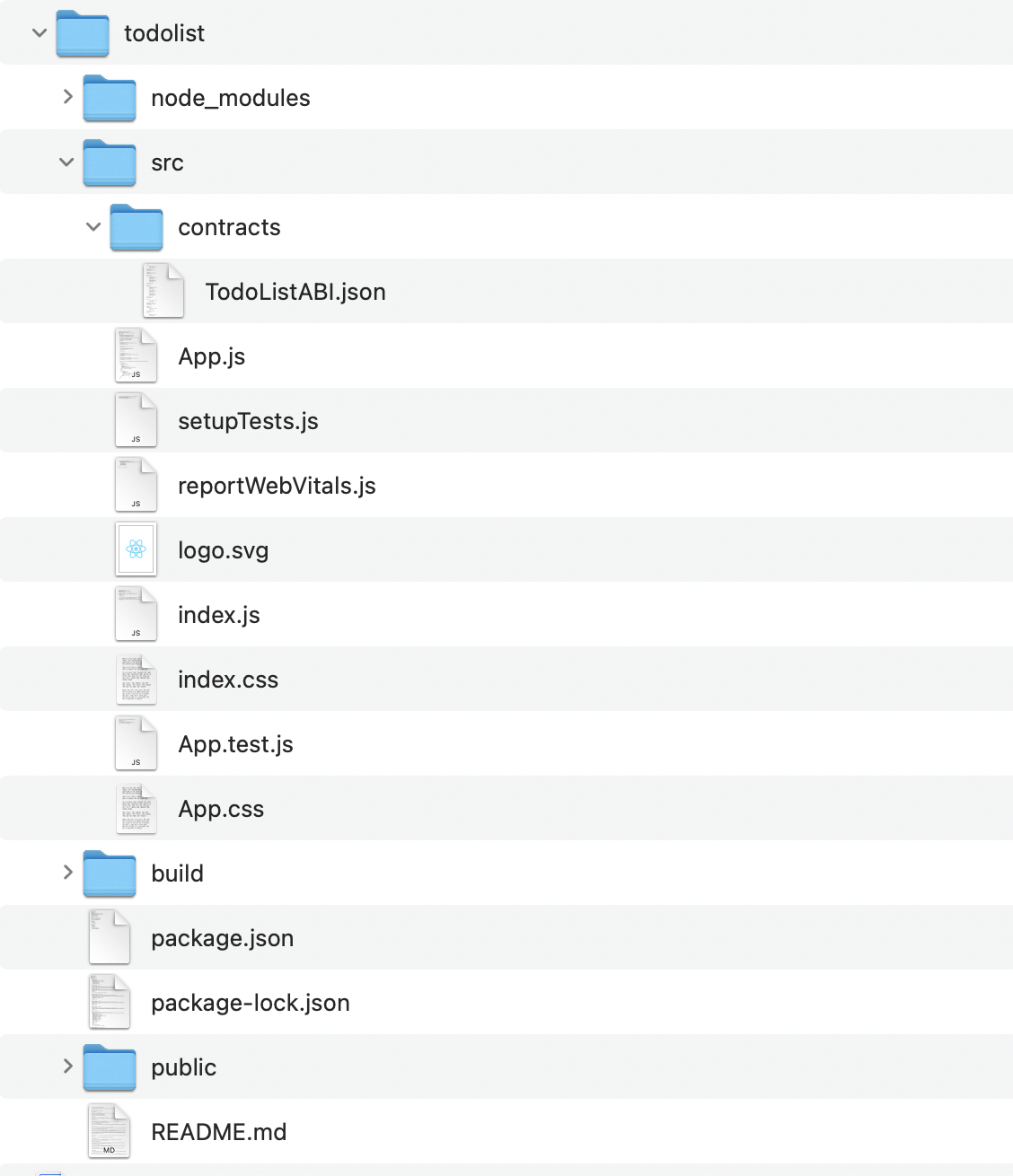
- In the App.js file, replace its content with the following:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
import TodoListABI from './contracts/TodoListABI.json';
import './App.css';
function App() {
const [tasks, setTasks] = useState([]);
const [taskContent, setTaskContent] = useState('');
const provider = new ethers.providers.Web3Provider(window.ethereum);
const signer = provider.getSigner();
const todoListContract = new ethers.Contract(
process.env.REACT_APP_TODO_LIST_ADDRESS,
TodoListABI,
signer
);
const getTasks = async () => {
const count = await todoListContract.taskCount();
const newTasks = [];
for (let i = 1; i <= count; i++) {
const task = await todoListContract.tasks(i);
newTasks.push(task);
}
setTasks(newTasks);
};
const createTask = async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
const { hash } = await todoListContract.createTask(taskContent);
await provider.waitForTransaction(hash);
await getTasks();
setTaskContent('');
};
const toggleCompleted = async (taskId) => {
const { hash } = await todoListContract.toggleCompleted(taskId);
await provider.waitForTransaction(hash);
await getTasks();
};
return (
<div className="App">
<h1>Todo List</h1>
<form onSubmit={createTask}>
<input
type="text"
placeholder="Add a Task"
value={taskContent}
onChange={(e) => setTaskContent(e.target.value)}
/>
<button type="submit">Add</button>
</form>
<div>
{tasks.map((task) => (
<div key={task.id}>
<input
type="checkbox"
checked={task.completed}
onChange={() => toggleCompleted(task.id)}
/>
<span>{task.content}</span>
</div>))
}
</div>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
- Test the dApp creation by using command:
npm start
Note: Remember to manually connect the todolist dApp to your wallet. There is no verification that the Gobi network is using the correct dApp.
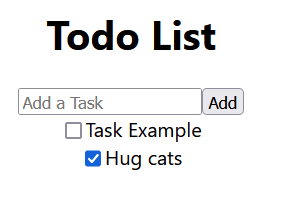
Playing with the dApp
The todolist dApp is displayed on your web browser (such as Chrome) using a localhost port. It is now functional. Play with the dApp by adding tasks and checking them off.
Note: If the dApp does not appear in your browser, then check the setting in your browser to allow JavaScript to be enabled. Also, make sure that your MetaMask wallet with the Gobi Testnet network is connected to the web browser.
Optional: Connection Fix
Use the following steps only if you are not able to add tasks and connect MetaMask to the Todo List dApp.
In the App.js file, use vi editor to perform the following:
- After the line:
function App(){
Add:
const [isConnected, setConnected] = useState(false);
Note: This line defines a state isConnected that updates with the setConnected modifier and sets to false.
- Before the line:
const getTasks = async () => {
Add:
const tryConnect = async () => {
const ret = await provider.send('eth_requestAccounts', []);
await getTasks();
setConnected(ret !== false);
}
Note: When tryConnect is called to connect to the local MetaMask accounts, it loads the todo tasks and updates the connection status.
- Before the line:
return (
<div className="App">
Add:
if (!isConnected) return <div className="App"><button onClick={tryConnect}>Connect</button></div>
Note: If the local MetaMask account is not connected, then this code snippet adds a button. This button calls tryConnect when it is clicked. If connected, the following code executes itself.
- Save the updates.